Hands-on training for medical education
Pfizer and 3spin Learning use virtual reality for the first time in Stroke Unit Starter Course
The "Medical Education Transfer" department, or meet for short, offers product-independent training for physicians. In doing so, it has ventured into as yet unexplored territory: For the "Stroke Unit Starter Course", the meet team has developed a virtual reality training course together with the startup 3spin Learning and Prof. Dr. Sobesky as well as Prof. Dr. Pfeilschifter from Frankfurt University Hospital.
VR pioneers in the field of medical training
Augmented or virtual reality has hardly been used for the training of healthcare professionals. Although there are initial attempts, the whole thing is still in its infancy – too complex, too expensive, in short: impractical. Gunter Lorenz, Medical Director Digital Science & Knowledge Management, and Servet Yilmaz, Customer Education Manager, and the meet team were not deterred by this. They saw the great potential of training medical processes in a realistic setting and set themselves the goal of taking medical training to a new level.
One area where well-rehearsed processes can make the difference between life and death is the treatment of stroke patients: When a stroke destroys millions of neurons, billions of synapses and kilometers of myelin fibers in the brain within minutes, every minute counts: According to a study entitled "One Minute – One Day," every minute saved from admission to the start of drug treatment to dissolve a blood clot saves an average of 1.8 additional healthy days of life. This means that the better the participants in an emergency department are coordinated, the more routine the procedures and the more precise the communication, the better it is for the patients.
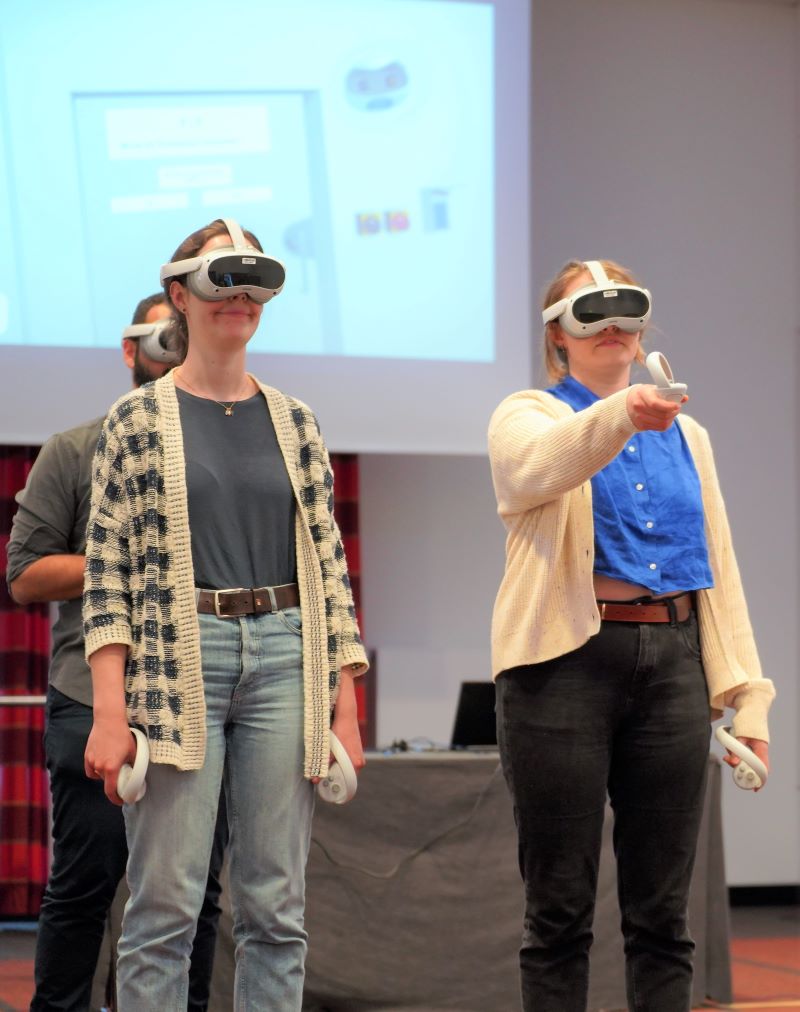

Learning by doing
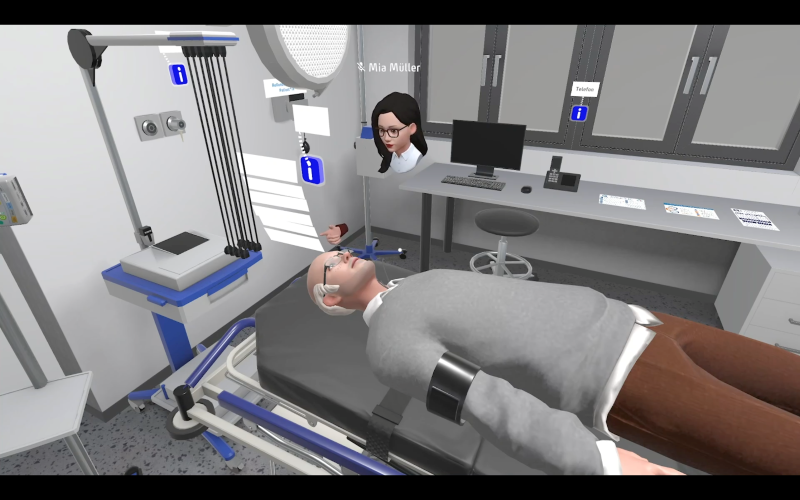
"Today, we often learn theoretically what actually needs to be practiced practically", says Thomas Hoger, CEO of 3spin Learning. The virtual reality training enables medical professionals to practice processes under realistic conditions instead of having to apply the theory in an emergency. In the VR-based training for the treatment of stroke patients, the participants wear VR goggles and virtually find themselves either in the shock room of an emergency room or in the CT examination room. Via controllers in their hands, they can perform activities and see not only the hands of their own avatar, but also the head and hands of the other team members. Together, the individual steps in the emergency room, for example, are played through and practiced under quasi-real conditions – medical teams thus have the chance to optimize these procedures under test conditions.
A glimpse into the VR environment of the Stroke Unit Starter Course:
Faster treatment through simulation-based training
A study at seven German university hospitals has shown that training can actually optimize interaction: It resulted in significantly shorter door-to-groin times for patients treated by teams with simulation experience compared to teams without such experience. "Door-to-groin is the time between admission and the start of treatment to remove a blood clot. Teams without simulation experience need an average of 95 minutes for this. With simulation experience, the average is 74 minutes, a difference of 21 minutes.
VR training for medical professionals: Too complex? Too expensive?
One of the biggest hurdles to using VR and AR for medical training has always been the high effort and associated costs for programming the virtual learning environment and training, IT integration and distribution. The startup 3spin Learning from Darmstadt has developed a clever solution for this: Instead of having IT prfoessionals translate the complex training content into code, 3spin Learning has developed cloud-based no-code software that allows medical experts to create and edit the training content themselves within a graphical user interface – making VR and AR training simple, affordable and scalable. "In today's creator economy, more young people want to become YouTubers than astronauts", said Thomas Hoger. "Through the 3spin Learning learning platform, we offer physicians a user-friendly platform to teach medical content in a professional way. The programming of the learning content is decoupled from the creation. The platform is also cloud-based. Scaling, even across multiple locations, is therefore straightforward."
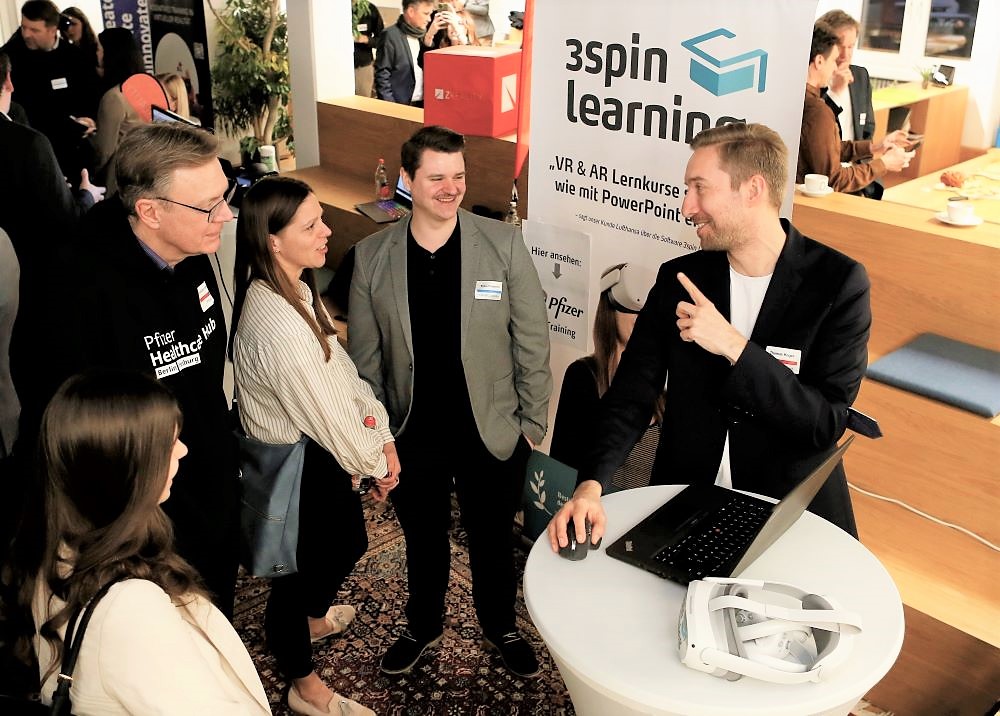
3spin Learning at VR Business Club Event in Breisach
At the VR Business Club on the topic of virtual reality, which took place in Breisach in February, the Pfizer Healthcare Hub offered the startup a tri-national stage on which it could present its learning platform to a select audience of experts. Interest was high both within the Pfizer organization and among potential users from the healthcare industry.

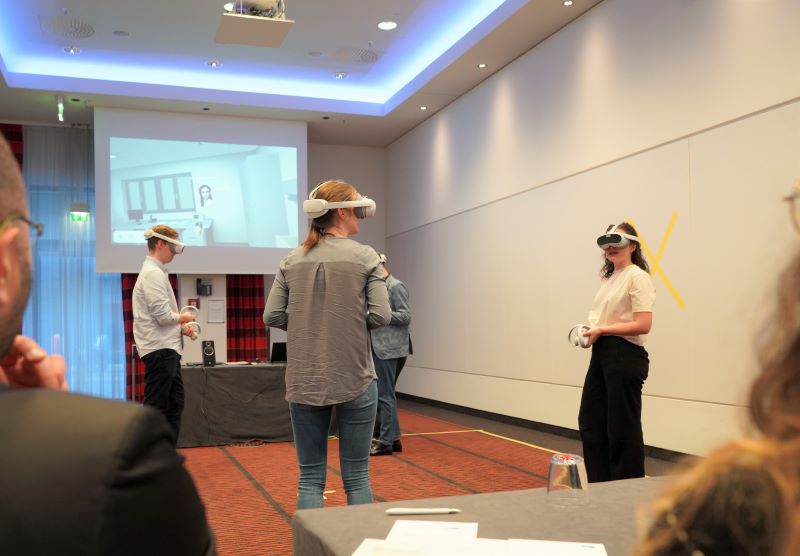
First VR Project for Pfizer Germany in Cooperation with 3spin Learning
In May 2023, the first virtual reality training took place at the "Stroke Unit Starter Course": Around 80 participants practiced all processes and actions in their role as neurologist, radiologist, patient, nurse or observer – from emergency admission, anamnesis and imaging to the start of therapy.

With the first VR project for Pfizer in Germany, 3spin Learning has now created the basis with which other process trainings can also be easily created. Servet Yilmaz sees a lot of potential in VR technology for other therapeutic areas, for example in the field of oncology or vaccines: "With this project, we have shown that VR training is not only practicable, but how much doctors and patients benefit from it. I am convinced that other departments at Pfizer can – and should – also exploit the potential from this in the future."
The common project was also a benefit for 3spin Learning: "The collaboration with Pfizer was a great opportunity for us to further develop the functionalities in the area of interaction and collaboration in our VR platform. From now on, physicians can act together in a training session and solve tasks collaboratively. We've also added configurable avatars to our multiplayer mode, which massively facilitates communication and helps participants get into character," says Annica Stähly, manager at 3spin Learning.
Sources:
Bohmann FO et al. Simulation-Based Training of the Rapid Evaluation and Management of Acute Stroke (STREAM) – A Prospective Single-Arm Multicenter Trial. https://pubmed.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/31572288/
Meretoja A et al. Stroke thrombolysis: save a minute, save a day. https://pubmed.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/24627114/